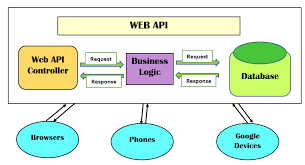
Web APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are essential components in modern web development, enabling different software systems to communicate and share data. They serve as intermediaries that allow developers to build applications that can interact with other services, databases, and platforms. This article explores what web APIs are, their types, benefits, and how to effectively use them in development.
What is a Web API?
A web API is a set of rules and protocols that allows one software application to interact with another over the internet. It defines the methods and data formats that applications can use to request and exchange information. Web APIs typically use HTTP as the communication protocol and are commonly represented in formats such as JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) or XML (eXtensible Markup Language).
4 Types of Web APIs
- REST APIs: Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs are based on a stateless, client-server architecture. They use standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) for operations and typically return data in JSON format. REST APIs are widely used due to their simplicity and scalability.
- SOAP APIs: Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) APIs are protocol-based and rely on XML for message format. SOAP APIs are known for their strict standards and are often used in enterprise-level applications requiring high security and reliability.
- GraphQL APIs: GraphQL is a query language for APIs that allows clients to request only the data they need. It enables developers to define the structure of the response, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching of data.
- WebSocket APIs: WebSocket APIs provide a persistent connection between the client and server, allowing real-time communication. This is particularly useful for applications that require live updates, such as chat applications or stock trading platforms.
Benefits of Using Web APIs
- Interoperability: APIs allow different applications, services, and platforms to work together seamlessly. This interoperability enables developers to integrate third-party services, enhancing functionality without building everything from scratch.
- Modularity: By using APIs, developers can create modular applications. Each component can be developed, maintained, and updated independently, leading to improved scalability and flexibility.
- Faster Development: APIs provide pre-built functionalities that developers can leverage, reducing the time needed to implement certain features. This allows teams to focus on building unique aspects of their applications.
- Access to External Data: APIs enable applications to access external data sources, such as social media platforms, payment gateways, and weather services. This can enrich user experiences by integrating diverse data and services.
- Security: APIs often include authentication and authorization mechanisms, allowing developers to control access to their services. This helps protect sensitive data and ensures that only authorized users can interact with the application.
How to Use Web APIs Effectively
- Understand the Documentation: API documentation provides essential information on how to use the API, including endpoints, request methods, parameters, and response formats. Thoroughly understanding the documentation is crucial for successful integration.
- Use API Clients: API clients, such as Postman or Insomnia, allow developers to test API endpoints easily. These tools help simulate requests and responses, making it easier to debug and explore APIs before integration.
- Handle Errors Gracefully: Implement robust error handling to manage API failures. This includes parsing error messages, implementing retries, and providing meaningful feedback to users when something goes wrong.
- Optimize Performance: Optimize API calls by reducing the number of requests and minimizing data transfer. Consider implementing caching strategies to store frequently accessed data and reduce the load on the API.
- Secure Your API: Implement security measures such as API keys, OAuth tokens, and HTTPS to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Regularly review security protocols to stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities.
- Monitor API Usage: Use analytics tools to monitor API usage and performance. Understanding how the API is being used can help identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
Real-World Examples of Web APIs
- Social Media APIs: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram offer APIs that allow developers to access user data, post updates, and interact with their services programmatically.
- Payment APIs: Services like PayPal and Stripe provide APIs for processing payments securely. Developers can integrate these APIs to handle transactions without having to build their own payment systems.
- Weather APIs: APIs from weather services allow applications to access real-time weather data, forecasts, and alerts, enriching user experiences with relevant information.
- Mapping APIs: Google Maps API provides developers with tools to integrate mapping and location services into their applications, allowing for features like geolocation and route planning.
Conclusion
Web APIs are fundamental to modern web development, enabling seamless communication between applications and services. By understanding the types of APIs, their benefits, and best practices for integration, developers can create powerful, interconnected applications that enhance user experiences and streamline workflows. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, leveraging web APIs will be crucial for building innovative solutions that meet user needs.